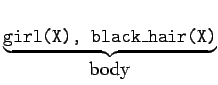CSc 372 - Comparative Programming Languages
16 : Prolog -- Introduction
Christian Collberg
Department of Computer Science
University of Arizona
- Prolog is a language which approaches problem-solving in a
declarative manner. The idea is to define what
the problem is, rather than how it should be solved.
- In practice, most Prolog programs have a procedural as
well as a declarative component -- the procedural
aspects are often necessary in order to make the programs
execute efficiently.
Algorithm = Logic + Control Robert A. Kowalski
- Prescriptive Languages:
-
- Describe how to solve problem
- Pascal, C, Ada,...
- Also: Imperative, Procedural
- Descriptive Languages:
-
- Describe what should be done
- Also: Declarative
Kowalski's equation says that
- Logic - is the specification (what the program should do)
- Control - what we need to do in order to make our
logic execute efficiently. This usually includes
imposing an execution order on the rules that make up our program.
Prolog programs deal with
- objects, and
- relationships between objects
English:
``Christian likes the record''
Prolog:
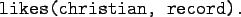
- Here's an excerpt from Christian's record database:

- The data base contains unary facts (is_record) and
binary facts (recorded_by, recording_year).
- The fact
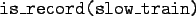
can be interpreted as
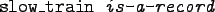
- The fact recording_year(slow_train, 1979) can be interpreted as
the recording year of slow_train was 1979.
- Prolog programs deal with conditional relationships between objects.
English:
``C. likes Bob Dylan records recorded before 1979''
Prolog:
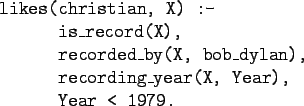
- The rule

can be restated as
``Christian likes X, if X is a
record, and X is recorded by Bob Dylan,
and the recording year is before 1979.''
- Variables start with capital letters.
- Comma (``,'') is read as and.
Prolog programs
- solve problems by asking questions.
English:
``Does Christian like the albums Planet Waves
& Slow Train?'
Prolog:

English:
``Was Planet Waves recorded by Bob Dylan?''
``When was Planet Waves recorded?''
``Which album was recorded in 1974?''
Prolog:

In Prolog
- "," (a comma), means "and'
English:
``Did Bob Dylan record an album in 1974?''
Prolog:
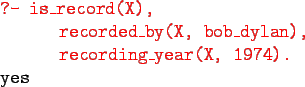
Sometimes a query has more than one answer:
- Use ";" to get all answers.
English:
``What does Christian like?''
Prolog:
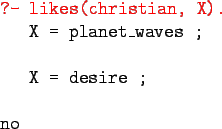
Sometimes answers have more than one part:
English:
``List the albums and their artists!''
Prolog:

``People are influenced by the music they listen to.
People are influenced by the music
listened to by the people they listen to.''

English:
``Is Björk influenced by Bob Dylan?''
``Is Björk influenced by Woody Guthrie?''
``Is Bob Dylan influenced by Bruce Springsteen?''
Prolog:

- Comma (,) is read as and in Prolog.
Example: The rule
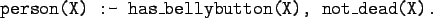
is read as
``X is a person if X has a bellybutton and
X is not dead.''
- Semicolon (;) is read as or in Prolog.
The rule
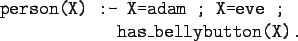
is read as
``X is a person if X is adam or X is eve or
X has a bellybutton.''
- To visualize what happens when Prolog executes (and this can
often be very complicated!) we use the following two
notations:
- For AND, both legs have to succeed.
- For OR, one of the legs has to succeed.
| AND |
OR |
| |
|
| and-example |
or-example |
- and and or can be combined:
and-or-example
- This query asks
``Is there a person X who is adam, eve, or who
has a bellybutton, and who is also not dead?''

- The rule (5) states that
``Every scientist is a logician''
- The question (6) asks
``Which scientist is a logician and an american?''
logician-3
logician

logician-2

likes

bjork1
bjork2
ColoringMap1
``Color a planar map with at most four colors,
so that contiguous regions are colored differently.''
A coloring is OK iff
- The color of Region 1
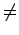 the color of Region 2, and
the color of Region 2, and
- The color of Region 1
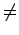 the color of Region 3,...
the color of Region 3,...


ColoringMap2
ColoringMap3
- gprolog can be downloaded from here: http://gprolog.inria.fr/.
- gprolog is installed on lectura (it's also on the
Windows machines) and is invoked like this:
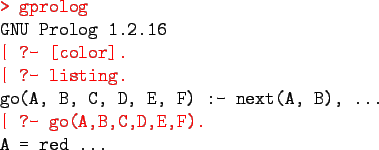
- The command [color] loads the prolog program in the
file color.pl.
- You should use the texteditor of your choice (emacs, vi,...) to write your prolog code.
- The command listing lists all the prolog predicates
you have loaded.
| Prolog by Example |
Coelho & Cotta |
| Prolog: Programming for AI |
Bratko |
| Programming in Prolog |
Clocksin & Mellish |
| The Craft of Prolog |
O'Keefe |
| Prolog for Programmers |
Kluzniak & Szpakowicz |
| Prolog |
Alan G. Hamilton |
| The Art of Prolog |
Sterling & Shapiro |
| Computing with Logic |
Maier & Warren |
| Knowledge Systems Through Prolog |
Steven H. Kim |
| Natural Language Processing in Prolog |
Gazdar & Mellish |
| Language as a Cognitive Process |
Winograd |
| Prolog and Natural Language Analysis |
Pereira and Shieber |
| Computers and Human Language |
George W. Smith |
| Introduction to Logic |
Irving M. Copi |
| Beginning Logic |
E.J.Lemmon |
- A Prolog program consists of a number of clauses:
- Rules
- Have head + body:
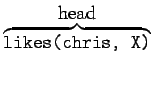 :-
:-
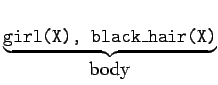
- Can be recursive
- Facts
- Head but no body.
- Always true.
- A clause consists of
- atoms
- Start with lower-case letter.
- variables
- Start with upper-case letter.
- Prolog programs have a
- Declarative meaning
- The relations defined by the program
- Procedural meaning
- The order in which goals are tried
- A question consists of one or more goals:
- ?- likes(chris, X), smart(X).
- "," means and
- Use ";" to get all answers
- Questions are either
- Satisfiable (the goal succeeds)
- Unsatisfiable (the goal fails)
- Prolog answers questions (satisfies goals) by:
- instantiating variables
- searching the database sequentially
- backtracking when a goal fails
Christian S. Collberg
2005-10-05





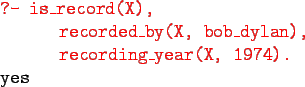
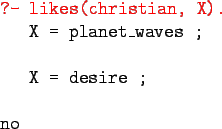









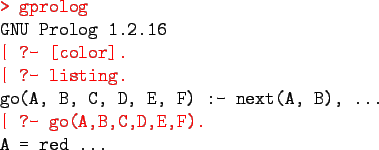
:-