CSc 372 - Comparative Programming Languages
11 : Haskell -- Higher-Order Functions
Christian Collberg
Department of Computer Science
University of Arizona
- A function is Higher-Order if it takes a
function as an argument or returns one as its
result.
- Higher-order function aren't weird;
the differentiation operation from high-school
calculus is higher-order:
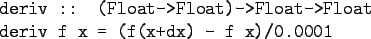
- Many recursive functions share a similar
structure. We can capture such
``recursive patterns'' in a
higher-order function.
- We can often avoid the use of
explicit recursion by using higher-order functions.
This leads to functions that are shorter, and
easier to read and maintain.
- We have already seen a number of higher-order functions.
In fact, any curried function
is higher-order. Why? Well, when a curried function
is applied to one of its arguments it returns a new
function as the result.
Uh, what was this currying thing?
- A curried function does not have to be applied to all its
arguments at once. We can supply some of the arguments,
thereby creating a new specialized function. This function
can, for example, be passed as argument
to a higher-order function.
How is a curried function defined?
- A curried function of
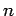 arguments (of types
arguments (of types
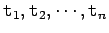 ) that
returns a value of type t is defined
like this:
) that
returns a value of type t is defined
like this:
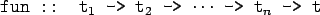
- This is sort of like defining
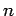 different functions
(one for each ->). In fact, we could define
these functions explicitly, but that would be tedious:
different functions
(one for each ->). In fact, we could define
these functions explicitly, but that would be tedious:
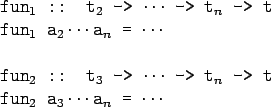
Duh, how about an example?
- Certainly. Lets define a recursive function get_nth n xs
which returns the n:th element from the list xs:
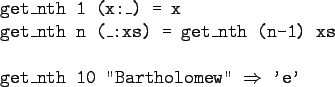
- Now, let's use get_nth to define functions
get_second, get_third, get_fourth,
and get_fifth, without using explicit recursion:
![\begin{gprogram}
get\_fifth ''Bartholomew'' $\Rightarrow$\ 'h' \\
\\
map (get\...
... [''mob'',''sea'',''tar'',''bat''] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x ''bart''
\end{gprogram}](img9.gif)
So, what's the type of get_second?
- Remember the Rule of Cancellation?
- The type of get_nth is Int -> [a] -> a.
- get_second applies get_nth to one
argument. So, to get the type of get_second
we need to cancel get_nth's first type:
Int
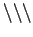 -> [a] -> a
-> [a] -> a
 [a] -> a.
[a] -> a.
Mappings
- Apply a function
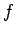 to the elements
of a list
to the elements
of a list 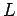 to make a new list
to make a new list 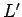 .
Example: Double the elements of an integer list.
.
Example: Double the elements of an integer list.
Selections
- Extract those elements from a list
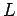 that satisfy a predicate
that satisfy a predicate 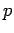 into a new list
into a new list 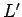 .
Example: Extract the even elements from an integer list.
.
Example: Extract the even elements from an integer list.
Folds
- Combine the elements of a list
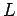 into
a single element using a binary function
into
a single element using a binary function 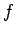 .
Example: Sum up the elements in an integer list.
.
Example: Sum up the elements in an integer list.
- map takes two arguments, a function and
a list. map creates a new list
by applying the function to each element of
the input list.
- map's first argument is a function
of type a -> b. The second argument is
a list of type [a]. The result is a list
of type [b].
![\begin{gprogram}
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b] \\
map f [\ ] \xxxxxx = [\ ] \\
map f (x:xs) \xxxxxx = f x : map f xs
\end{gprogram}](img16.gif)
- We can check the type of an object using the
:type command. Example: :type map.
![\begin{gprogram}
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b] \\
map f [\ ] \xxxxxx = [\ ] \\
map f (x:xs) \xxxxxx = f x : map f xs
\end{gprogram}](img16.gif)
- map f [ ] = [ ]
- means:
``The result of applying the function f
to the elements of an empty list is the empty list.''
- map f (x:xs) = f x : map f xs
- means:
``applying f to the list (x:xs) is the
same as applying f to x (the first
element of the list), then applying f to
the list xs, and then combining the results.''
Simulation:
![\begin{gprogram}
map square [5,6] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x square 5 : map square [6...
...) $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\xx 25 : [36] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [25,36]
\end{gprogram}](img18.gif)
- Filter takes a predicate
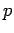 and a list
and a list 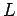 as arguments. It returns a list
as arguments. It returns a list 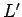 consisting
of those elements from
consisting
of those elements from 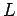 that satisfy
that satisfy 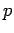 .
.
- The predicate
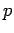 should have the type
a -> Bool, where a is the
type of the list elements.
should have the type
a -> Bool, where a is the
type of the list elements.
Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{filter even [1..10]} $\Rightarrow$\ [2,4,6,8,10] \\
\r...
...\\
\x \redtxt{where gt10 x = x > 10} $\Rightarrow$\ [11,23,114]
\end{gprogram}](img19.gif)
- We can define filter using either recursion or list
comprehension.
Using recursion:
![\begin{gprogram}
filter :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [a] \\
filter \_ [] = [] \\
f...
...xxxx = x : filter p xs \\
\x \vert otherwise \xxxx = filter p xs
\end{gprogram}](img20.gif)
Using list comprehension:
![\begin{gprogram}
filter :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [a] \\
filter p xs = [x \vert x <- xs, p x]
\end{gprogram}](img21.gif)
- doublePos doubles the positive integers in a list.
![\begin{gprogram}
getEven :: [Int] -> [Int] \\
getEven xs = filter even xs \\
\...
...r pos xs) \\
\x where \= dbl x = 2 * x \\
\x \x pos x = x > 0
\end{gprogram}](img23.gif)
Simulations:
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{getEven [1,2,3]} $\Rightarrow$\ [2] \\
\\
\redtxt{dou...
...,2,3,4]) $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x map dbl [2,4] $\Rightarrow$\ [4,8]
\end{gprogram}](img24.gif)
- A common operation is to combine the elements
of a list into one element. Such operations are
called reductions or accumulations.
Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
sum [1,2,3,4,5] $\equiv$\ \\
\xx (1 + (2 + (3 + (4 + (5 + 0)))...
...
\xx (''H'' ++ (''i'' ++ (''!'' ++ ''''))) $\Rightarrow$\ ''Hi!''
\end{gprogram}](img25.gif)
- Notice how similar these operations are.
They both combine the elements in a
list using some binary operator (+, ++),
starting out with a ``seed'' value
(0, "").
- Haskell provides a function foldr (``fold right'')
which captures this pattern of computation.
- foldr takes three arguments: a function,
a seed value, and a list.
Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{foldr (+) 0 [1,2,3,4,5]} $\Rightarrow$\ 15 \\
\redtxt{foldr (++) '''' [''H'',''i'',''!'']} $\Rightarrow$\ ''Hi!''
\end{gprogram}](img26.gif)
foldr:
![\begin{gprogram}
foldr :: (a->b->b) -> b -> [a] -> b \\
foldr f z [\ ] \xxxxxx = z \\
foldr f z (x:xs) \xxxxxx = f x (foldr f z xs)
\end{gprogram}](img27.gif)
- Note how the fold process is started by
combining the last element
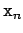 with
z. Hence the name seed.
with
z. Hence the name seed.
- Several functions in the standard prelude
are defined using foldr:
![\begin{gprogram}
and,or :: [Bool] -> Bool \\
and xs = foldr (\&\&) True xs \\
or xs = foldr (\vert\vert) False xs
\end{gprogram}](img30.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{? or [True,False,False]} $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x foldr (\...
...t (False \vert\vert (False \vert\vert False)) $\Rightarrow$\ True
\end{gprogram}](img31.gif)
- Remember that foldr binds from the right:
![\begin{gprogram}
foldr (+) 0 [1,2,3] $\Rightarrow$\ (1+(2+(3+0)))
\end{gprogram}](img32.gif)
- There is another function foldl that binds from the left:
![\begin{gprogram}
foldl (+) 0 [1,2,3] $\Rightarrow$\ (((0+1)+2)+3)
\end{gprogram}](img33.gif)
- In the case of (+) and many other
functions
- However, one version may be more efficient than the other.
fold
- We've already seen that it is possible to use
operators to construct new functions:
- (*2) -
- function that doubles its argument
- (>2) -
- function that returns True for
numbers
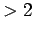 .
.
- Such partially applied operators are know as
operator sections. There are two kinds:
(op a) b = b op a
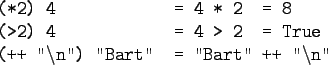
(a op) b = a op b
![\begin{gprogram}
(3:) [1,2] \xxxx = 3 : [1,2] \xxxx = [3,1,2] \\
(0<) 5 \xxxx = 0 < 5 \xxxx = True \\
(1/) \xxxx = 1/5
\end{gprogram}](img38.gif)
Examples:
- (+1) -
- The successor function.
- (/2) -
- The halving function.
- (:[]) -
- The function that turns an
element into a singleton list.
More Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{? filter (0<) (map (+1) [-2,-1,0,1])} \\
\x [1,2]
\end{gprogram}](img39.gif)
- We've looked at the list-breaking functions
drop & take:
![\begin{gprogram}
take 2 ['a','b','c'] $\Rightarrow$\ ['a','b'] \\
drop 2 ['a','b','c'] $\Rightarrow$\ ['c']
\end{gprogram}](img40.gif)
- takeWhile and dropWhile are
higher-order list-breaking functions. They
take/drop elements from a list while a
predicate is true.
![\begin{gprogram}
takeWhile even [2,4,6,5,7,4,1] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [2,4,6] \\
dropWhile even [2,4,6,5,7,4,1] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [5,7,4,1]
\end{gprogram}](img41.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
takeWhile :: (a->Bool) -> [a] -> [a] \\
takeWhile p [\ ] = [\ ...
...rt p x \xxxx = dropWhile p xs \\
\x \vert otherwise \xxxx = x:xs
\end{gprogram}](img42.gif)
- Remove initial/final blanks from a string:
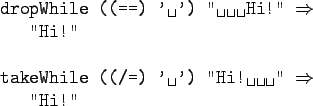
- Higher-order functions take functions
as arguments, or return a function as
the result.
- We can form a new function by
applying a curried function to some (but not all) of
its arguments. This is called partial application.
- Operator sections are partially applied
infix operators.
- The standard prelude contains many useful
higher-order functions:
- map f xs
- creates a new list by applying
the function f to every
element of a list xs.
- filter p xs
- creates a new list by selecting
only those elements from xs
that satisfy the predicate p
(i.e. (p x) should return True).
- foldr f z xs
- reduces a list xs
down to one element, by applying the binary
function f to successive elements,
starting from the right.
- scanl/scanr f z xs
- perform the same
functions as foldr/foldl, but instead of
returning only the ultimate value they return
a list of all intermediate results.
Homework (a):
- Define the map function using a
list comprehension.
Template:
![\begin{gprogram}
map f x = [ $\cdots$\ \vert $\cdots$\ ]
\end{gprogram}](img44.gif)
Homework (b):
- Use map to define a function lengthall xss
which takes a list of strings xss as argument
and returns a list of their lengths as result.
Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{? lengthall [''Ay'', ''Caramba!'']} \\
\x [2,8]
\end{gprogram}](img45.gif)
- Give a accumulative recursive definition of foldl.
- Define the minimum xs function using foldr.
- Define a function sumsq n that returns the sum
of the squares of the numbers
![$[1\cdots n]$](img46.gif) . Use
map and foldr.
. Use
map and foldr.
- What does the function mystery below do?
![\begin{gprogram}
mystery xs = \\
\x foldr (++) [] (map sing xs)\\
sing x = [x]
\end{gprogram}](img47.gif)
Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
minimum [3,4,1,5,6,3] $\Rightarrow$\ 1
\end{gprogram}](img48.gif)
- Define a function zipp f xs ys that
takes a function f and two
lists xs=[
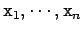 ] and
ys=[
] and
ys=[
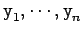 ] as argument,
and returns the list
[
] as argument,
and returns the list
[
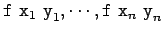 ]
as result.
]
as result.
- If the lists are of unequal length, an error should be
returned.
Examples:
![\begin{gprogram}
zipp (+) [1,2,3] [4,5,6] $\Rightarrow$\ [5,7,9] \\
\\
zipp (=...
...ue] \\
\\
zipp (==) [1,2,3] [4,2] $\Rightarrow$\ \redtxt{ERROR}
\end{gprogram}](img52.gif)
- Define a function filterFirst p xs that
removes the first element of xs that does not
have the property p.
Example:
![\begin{gprogram}
filterFirst even [2,4,6,5,6,8,7] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [2,4,6,6,8,7]
\end{gprogram}](img53.gif)
- Use filterFirst to define a function
filterLast p xs that
removes the last occurence of an element of xs
without the property p.
Example:
![\begin{gprogram}
filterLast even [2,4,6,5,6,8,7] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [2,4,6,5,6,8]
\end{gprogram}](img54.gif)
Christian S. Collberg
2005-09-16
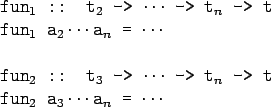
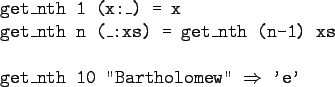
![\begin{gprogram}
get\_fifth ''Bartholomew'' $\Rightarrow$\ 'h' \\
\\
map (get\...
... [''mob'',''sea'',''tar'',''bat''] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x ''bart''
\end{gprogram}](img9.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b] \\
map f [\ ] \xxxxxx = [\ ] \\
map f (x:xs) \xxxxxx = f x : map f xs
\end{gprogram}](img16.gif)
![\begin{bprogram}
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b] \\
map f [\ ] \xxxxxx = [\ ] \\ ...
...
inc x = x + 1 \\
\\
map inc [1,2,3,4] $\Rightarrow$\ [2,3,4,5]
\end{bprogram}](img17.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b] \\
map f [\ ] \xxxxxx = [\ ] \\
map f (x:xs) \xxxxxx = f x : map f xs
\end{gprogram}](img16.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
map square [5,6] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x square 5 : map square [6...
...) $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\xx 25 : [36] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [25,36]
\end{gprogram}](img18.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{filter even [1..10]} $\Rightarrow$\ [2,4,6,8,10] \\
\r...
...\\
\x \redtxt{where gt10 x = x > 10} $\Rightarrow$\ [11,23,114]
\end{gprogram}](img19.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
filter :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [a] \\
filter \_ [] = [] \\
f...
...xxxx = x : filter p xs \\
\x \vert otherwise \xxxx = filter p xs
\end{gprogram}](img20.gif)
![]()
![\begin{bprogram}
filter :: (a->Bool)->[a]->[a] \\
filter \_ [] = [] \\
filter ...
... p xs \\
\\
\redtxt{filter even [1,2,3,4] $\Rightarrow$\ [2,4]}
\end{bprogram}](img22.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
getEven :: [Int] -> [Int] \\
getEven xs = filter even xs \\
\...
...r pos xs) \\
\x where \= dbl x = 2 * x \\
\x \x pos x = x > 0
\end{gprogram}](img23.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{getEven [1,2,3]} $\Rightarrow$\ [2] \\
\\
\redtxt{dou...
...,2,3,4]) $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x map dbl [2,4] $\Rightarrow$\ [4,8]
\end{gprogram}](img24.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
sum [1,2,3,4,5] $\equiv$\ \\
\xx (1 + (2 + (3 + (4 + (5 + 0)))...
...
\xx (''H'' ++ (''i'' ++ (''!'' ++ ''''))) $\Rightarrow$\ ''Hi!''
\end{gprogram}](img25.gif)
![]()
![\begin{gprogram}
foldr :: (a->b->b) -> b -> [a] -> b \\
foldr f z [\ ] \xxxxxx = z \\
foldr f z (x:xs) \xxxxxx = f x (foldr f z xs)
\end{gprogram}](img27.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
and,or :: [Bool] -> Bool \\
and xs = foldr (\&\&) True xs \\
or xs = foldr (\vert\vert) False xs
\end{gprogram}](img30.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
\redtxt{? or [True,False,False]} $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x foldr (\...
...t (False \vert\vert (False \vert\vert False)) $\Rightarrow$\ True
\end{gprogram}](img31.gif)
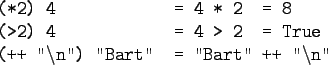
![\begin{gprogram}
(3:) [1,2] \xxxx = 3 : [1,2] \xxxx = [3,1,2] \\
(0<) 5 \xxxx = 0 < 5 \xxxx = True \\
(1/) \xxxx = 1/5
\end{gprogram}](img38.gif)
![]()
![]()
![\begin{gprogram}
takeWhile even [2,4,6,5,7,4,1] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [2,4,6] \\
dropWhile even [2,4,6,5,7,4,1] $\Rightarrow$\ \\
\x [5,7,4,1]
\end{gprogram}](img41.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
takeWhile :: (a->Bool) -> [a] -> [a] \\
takeWhile p [\ ] = [\ ...
...rt p x \xxxx = dropWhile p xs \\
\x \vert otherwise \xxxx = x:xs
\end{gprogram}](img42.gif)
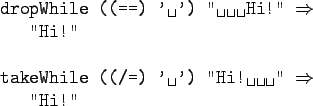
![]()
![\begin{gprogram}
mystery xs = \\
\x foldr (++) [] (map sing xs)\\
sing x = [x]
\end{gprogram}](img47.gif)
![]()
![\begin{gprogram}
zipp (+) [1,2,3] [4,5,6] $\Rightarrow$\ [5,7,9] \\
\\
zipp (=...
...ue] \\
\\
zipp (==) [1,2,3] [4,2] $\Rightarrow$\ \redtxt{ERROR}
\end{gprogram}](img52.gif)
![]()
![]()