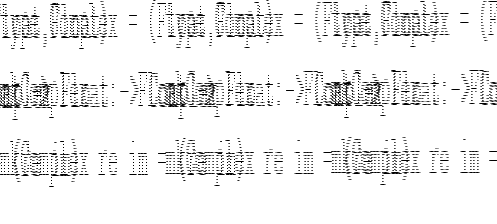
Christian Collberg
Department of Computer Science
University of Arizona

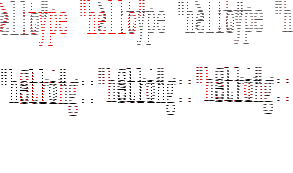
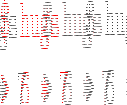
| Op | Precedence | Associativity | Description | |
^ |
8 | right | Exponentiation | |
| *, / | 7 | left | Mul, Div | |
| `div` | 7 | free | Division | |
| `rem` | 7 | free | Remainder | |
| `mod` | 7 | free | Modulus | |
| +, - | 6 | left | Add, Subtract | |
| ==,/= | 4 | free | (In-) Equality | |
<,<=,>,>= |
4 | free | Relational Comparison |
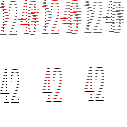


![]()
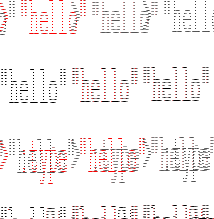
| Op | Precedence | Associativity | Description |
&& |
3 | right | logical and |
|| |
2 | right | logical or |
| not | 9 | - | logical not |
![]()


![\begin{program}
\redtt{> [1,2,3]} \\
{[1,2,3]}\\
\redtt{> [True,False] :: [Boo...
...\
\redtt{> [1,True]} \\
ERROR \\
\redtt{> length [1,2,3]} \\
3
\end{program}](img28.gif)
Examples: