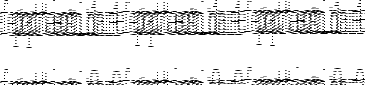
Christian Collberg
Department of Computer Science
University of Arizona
Pattern Syntax:
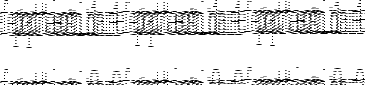

fact Revisited:
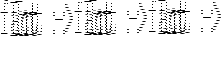
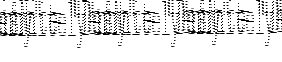
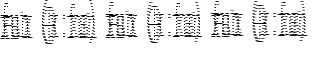
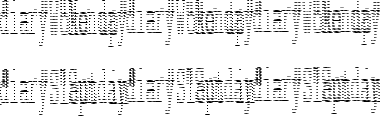
| Pattern | Syntax | Example | Description |
| variable | var_name | fact n = |
n matches any argument |
| constant | literal | fact 0 = |
matches the value |
| wildcard | _ | five _ = 5 | _ matches any argument |
| (n+k) pat. | (n+k) | fact (n+1) = |
(n+k) matches any integer |
| Pattern | Syntax | Example | Description |
| cons | (x:xs) | len (x:xs) = |
matches non-empty list |
| empty | [ ] | len [ ] = 0 | matches the empty list |
| one-elem | [x] | len [x] = 1 | matches a list with exactly 1 element. |
| two-elem | [x,y] | len [x,y] = 2 | matches a list with exactly 2 elements. |
Using conditional expr:
![\begin{gprogram}
sumlist :: [Int] -> Int \\
sumlist xs = \= if xs == [\ ] then 0 \\
\x else head xs + sumlist(tail xs)
\end{gprogram}](img11.gif)
Using patterns:
![\begin{gprogram}
sumlist :: [Int] -> Int \\
sumlist [\ ] = 0 \\
sumlist (x:xs) = x + sumlist xs
\end{gprogram}](img12.gif)
Using conditional expr:
![]()
Using patterns:
![\begin{gprogram}
len :: [Int] -> Int \\
len [\ ] = 0 \\
len (\_:xs) = 1 + len xs
\end{gprogram}](img14.gif)
Using conditional expr:
![]()
Using patterns:
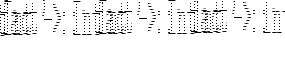

![\begin{gprogram}
member :: Int -> [Int] -> Bool \\
member x L = $\cdots$\ \\
\...
...[1,2,3]} \\
\x True \\
\redtxt{? member 4 [1,2,3]} \\
\x False
\end{gprogram}](img20.gif)
![\begin{gprogram}
memberNum :: Int -> [Int] -> Int \\
unique :: [Int] -> Int \\ ...
...[1,5,2,3,5,5]} \\
\x 3\\
\redtxt{? unique [2,4,2,1,4]} \\
\x 1
\end{gprogram}](img21.gif)