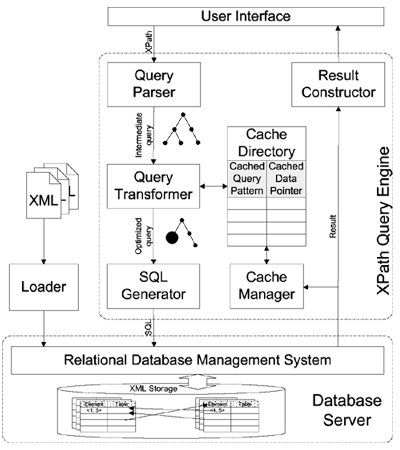
The XPath Query Engine, which
is located between the user interface and the database server, is the
core component of the XISS/R system. The query engine accepts XPath
queries and generates SQL statements to send to the database server.
Query results from the database server are then formated and forwarded
to the user interface by the query engine.
Upon receiving an XPath query, the Query
Parser first parses the query and translates it into an
intermediate tree-structured format. For example, the query A[B]/C will
be translated into a tree with node A as the root, and B and C as two
children of A.
This tree-structured intermediary is then simplified by the Query Transformer based on current
cache information in the Cache
Directory. The Cache Directory
stores result information from previous queries. Each entry in the
directory consists of a query pattern in tree-structured intermediate
format, and a pointer to it's associated result set.
The Query Transformer matches
the current query tree against patterns in the cache directory. If a
match is found, the matched part in the query tree will be replaced by
a super node. This super node is similar to a normal node except that
when parsed into SQL, the SQL
Generator will evaluate it based on cached results. For example,
if the result of the query A[B] is in the cache, the subtree
representing A[B] can be replaced by a super node representing cached
results. The query is thus simplified into a two-node query tree. In
addition, other optimizations can be implemented inside the Query Transformer.
The simplified query tree is translated into SQL statements by the SQL Translator and communicated to
the database server. For example, the query media[@media-type="image"]
will be translated into the following SQL statement when using Schema
A:
SELECT
et0.DID as Document, et0.NID as Node_ID
FROM
elem_tab et0, attr_tab at0
WHERE
et0.NAME = 'media' and
at0.NAME = 'media-type' and
at0.VALUE = 'image' and
at0.DID = et0.DID and
at0.PARENT_ID = et0.NID
The database server processes the SQL query and returns the result to
the XPath Query Engine, whose Result
Constructor formats the result and sends it to the user
interface for display. The result is also sent to the Cache Manager, which makes a
caching decision based on information such as result set and data size,
query pattern or sub-pattern frequency, query processing time, etc.
